Liquid cooling is a more efficient alternative to air cooling in data centers, particularly due to its ability to handle the higher heat loads generated by modern high-density computing environments. Here are some quantitative insights on the efficiency of liquid cooling compared to air cooling:
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Liquid cooling systems are significantly more efficient in heat dissipation compared to air cooling. They can absorb and carry away heat up to four times more effectively than air. This efficiency leads to substantial energy savings, with liquid cooling systems potentially reducing energy consumption by up to 90%. [8]
- Cooling Capacity: Liquid cooling can handle higher thermal densities effectively. This is crucial as data centers increasingly deploy high-performance computing resources that generate significant heat, which traditional air cooling systems might struggle to manage efficiently. [9]
- Increased Rack Density: Modern data centers experience a remarkable increase in rack power densities. A decade ago, average rack densities were around 4-5 kW, but they are now predicted to reach 15-20 kW and even higher in the future. [10] Liquid cooling effectively supports these higher densities, allowing for more compact and efficient data center designs. [8]
- Temperature Control and Reliability: Liquid cooling provides superior precision in temperature control, ensuring components operate within optimal temperature ranges. This reduces the risk of overheating and thermal throttling, thereby extending the lifespan of data center equipment and improving overall reliability. [8]
- Maintenance and Operational Cost Reduction: Liquid cooling systems generally require less maintenance than air cooling systems. The absence of dust and debris in liquid-cooled environments reduces the risk of component damage, and the closed-loop nature of many liquid cooling systems minimizes the need for frequent maintenance. Additionally, the elimination of extensive air conditioning systems can lead to significant operational cost savings.
- Liquid Cooling in Edge Computing and IoT: In edge computing and IoT applications, liquid cooling is becoming increasingly important. Edge computing sites often need to handle high-performance workloads such as data analytics and machine learning, which generate significant heat. Traditional air-cooled solutions may be insufficient in these scenarios, especially in remote or harsh environments where maintaining optimal temperatures is challenging. Liquid cooling, including solutions like direct-to-chip and immersion cooling, provides effective thermal management, ensuring reliability and performance of edge computing nodes
- Investment in Quieter Cooling: Liquid cooling is significantly quieter than air cooling because it doesn't rely on large fans, which typically generate more noise. This reduction in noise pollution is critical in dense computational environments like data centers, enhancing the operational environment and reducing auditory stress for maintenance and operational staff.
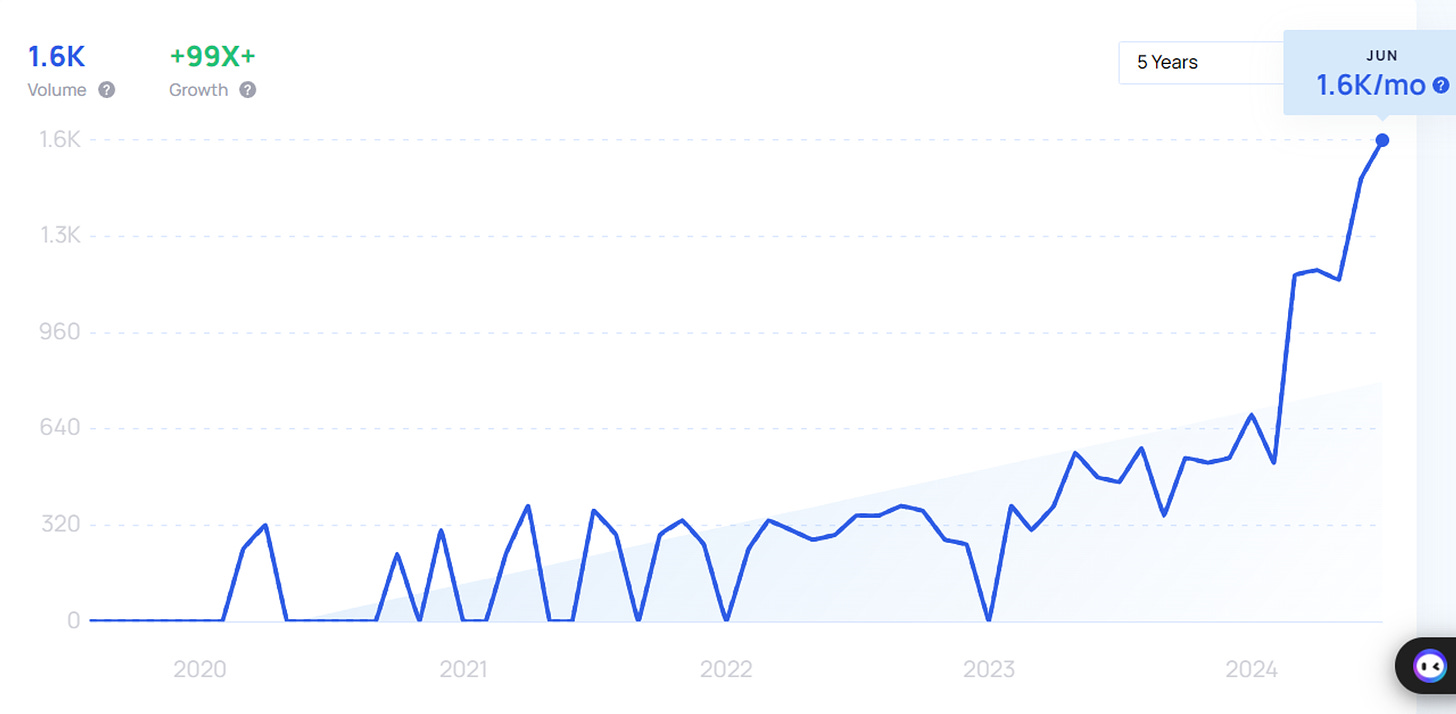
Figure 5: Based on Exploding Topics Liquid Cooling Data Center Trend, this sector is experiencing exploding growth in market sentiment.

