The U.S. federal government and local governments offer several incentives for lithium battery recycling to promote sustainable practices and reduce environmental impact. These incentives often come in the form of grants, tax credits, and regulatory benefits.
Tax Credits: The federal government provides tax incentives for businesses involved in the recycling of lithium-ion batteries under the Energy Policy Act. These may include investment credits or deductions for equipment and facility expenses related to battery recycling processes.
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) introduces significant regulations for electric vehicle (EV) battery manufacturing to qualify for federal tax credits. These regulations focus on the sourcing and manufacturing of critical minerals and components within the battery. To qualify for the full tax credit of up to $7,500, EVs must meet specific criteria:
Conclusion: While the U.S. has some mineral deposits and plans for refining capacity, the global mineral distribution and China's dominance make reliance solely on mining challenging. Fortunately, domestic requirements under the Clean Vehicle credit can also be met by recycling battery materials. Currently, the EV battery recycling industry is nascent, mainly processing production scrap rather than end-of-life batteries. However, with the Inflation Reduction Act potentially putting 37 million EVs on the road by 2032, recycling these batteries will become increasingly critical.
Grants and Funding: Agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Department of Energy (DOE) often offer grants aimed at advancing recycling technology and infrastructure, which include lithium battery recycling initiatives.

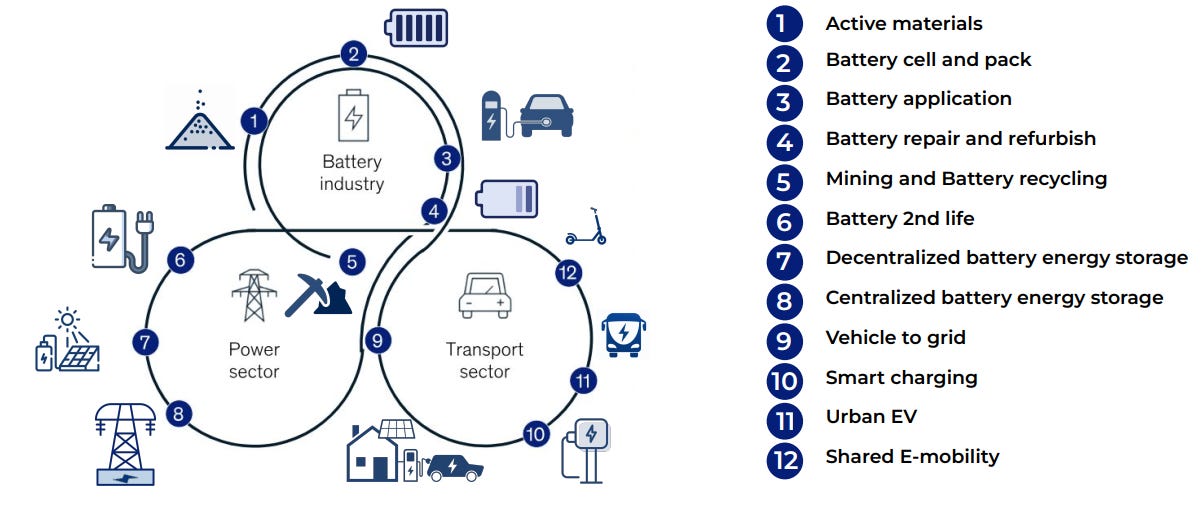
Figure 5: Circular Battery Value Chain: Expansion of global battery value chain is unlocking significant economic potential across multiple industries [11]