Scalability:
- Challenges: Both traditional liquid cooling components like radiator-based and AIO systems face scalability challenges when deployed in large data centers. Managing hundreds or thousands of individual cooling units is less efficient compared to centralized or more integrated cooling solutions.
- Solutions: Centralized systems like in-row cooling, chilled water systems, or advanced liquid cooling techniques such as direct-to-chip or immersion cooling are better suited for large-scale deployments. These solutions provide more uniform cooling and are easier to manage and scale.
Efficiency:
- Requirements: While air cooling has been the standard due to its relative flexibility and ease of use, it is failing to keep up with the heat output in modern server farms. Prior to the advent of more computation-intensive technologies, most server racks peaked at 20kW. Now, many push or exceed 30kW. Graphics processing units (GPUs), which support AI and machine learning technology, exceed 40kW. Air cooling simply cannot keep up with the heat generated by that level of power use.
- Advantages of Liquid Cooling: Advanced liquid cooling solutions, such as direct-to-chip and immersion cooling, offer superior heat dissipation and energy efficiency. These systems can handle higher thermal densities effectively, making them ideal for modern, high-performance data centers.
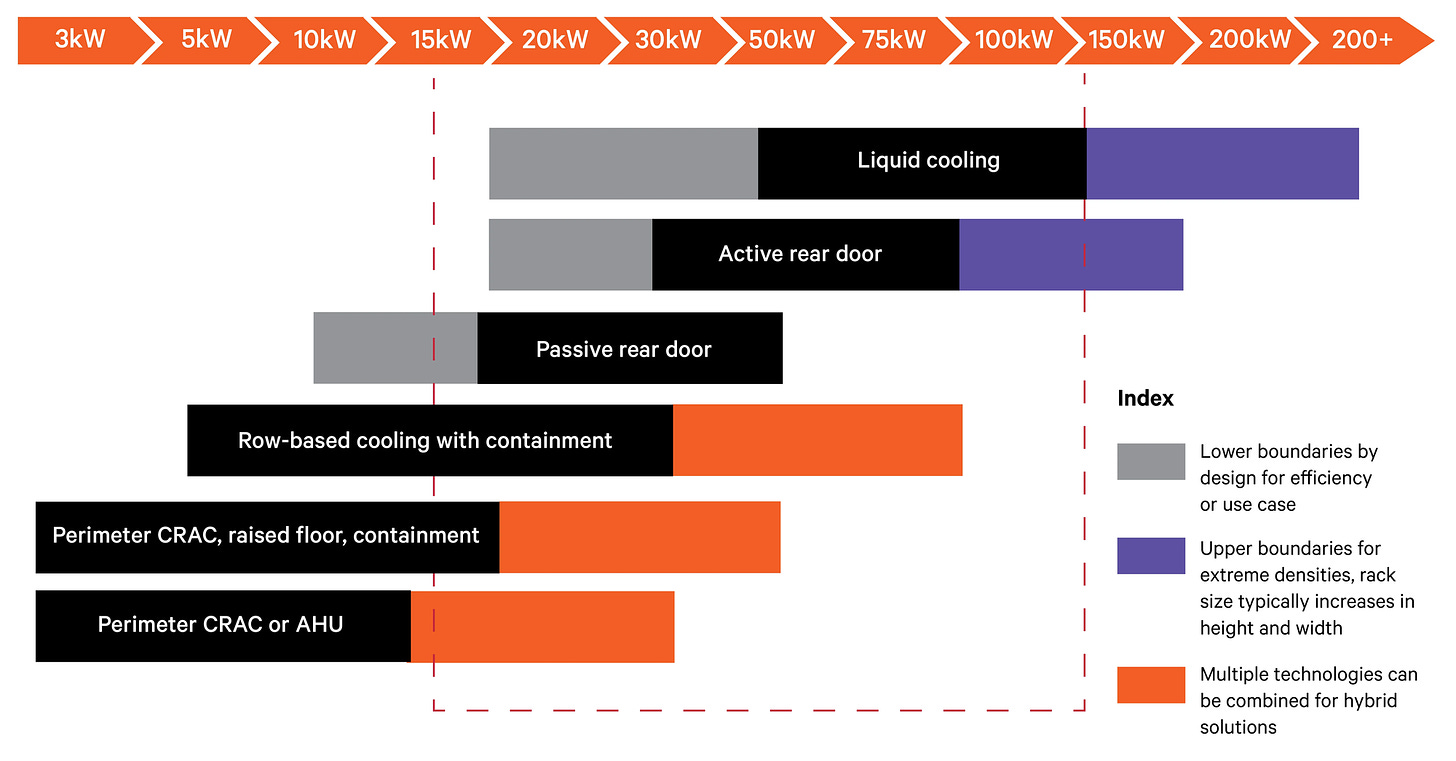
Figure 6: Liquid Cooling Versus Air Cooling: How Thermal Management Systems Are Evolving [1]
Space and Infrastructure:
- Space Constraints: Implementing radiator-based and AIO systems in large-scale data centers requires substantial space for radiators and associated infrastructure. This can potentially reduce the available space for actual computing hardware.
- Edge Data Centers: In edge data centers, where space is often limited and environmental conditions can be challenging, liquid cooling provides a compact and efficient solution. Edge data centers benefit from the enhanced cooling efficiency of liquid cooling systems, which can be more easily adapted to smaller, distributed sites.
- Integrated Solutions: More integrated cooling solutions like in-row cooling or liquid cooling systems minimize the footprint of cooling infrastructure, optimizing the use of space within the data center.
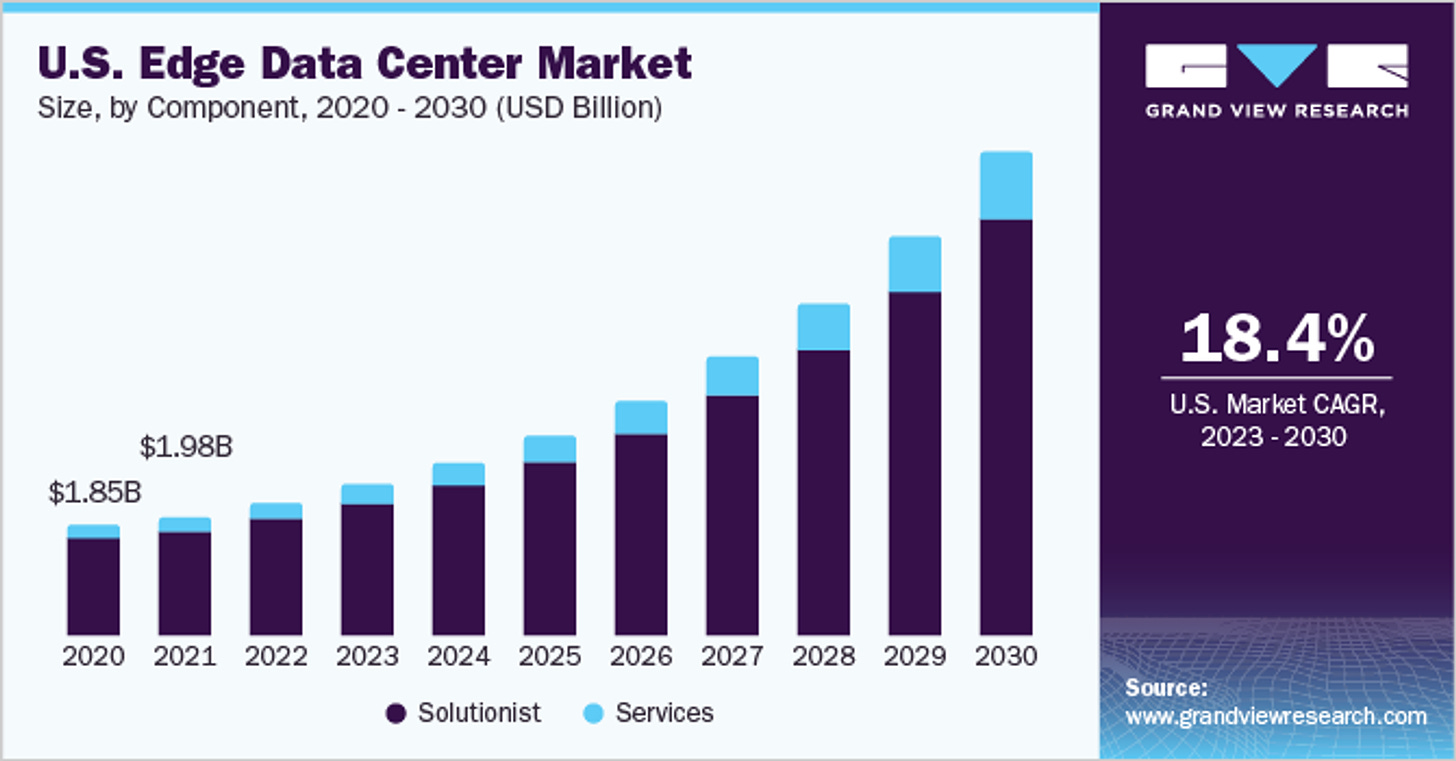
Figure 7: Edge Data Center Market Size & Trends [11]
Failure Rate:
- Reliability: Heat removal is far more consistent and uniform with advanced liquid cooling technology, leading to lower levels of equipment failure and consequent maintenance and replacement. Hotspots in server equipment are a persistent problem and all forms of liquid cooling appear to be superior to air cooling in mitigating or eliminating them. However, chilled water system, immersion cooling and direct to chip method do carry the risk of leakage. Chilled water systems have a higher risk of extensive damage due to potential water leaks affecting multiple components. D2C and immersion cooling systems are better contained and pose less risk of widespread damage. When the fluids are not conductive, leakage typically is not a major threat to IT equipment . But it will cause cooling systems to fail, leading to possible overheating.
- Financial Impact: Data center failures can be extremely costly. Over 60% of failures result in at least $100,000 in total losses, the share of outages that cost upwards of $1 million increased is around 15%. [12] Cooling system failures are a significant cause of data center outages, contributing to approximately 14% of all data center failures. [13] Reducing the risk of these failures through more reliable cooling methods can result in substantial financial savings.
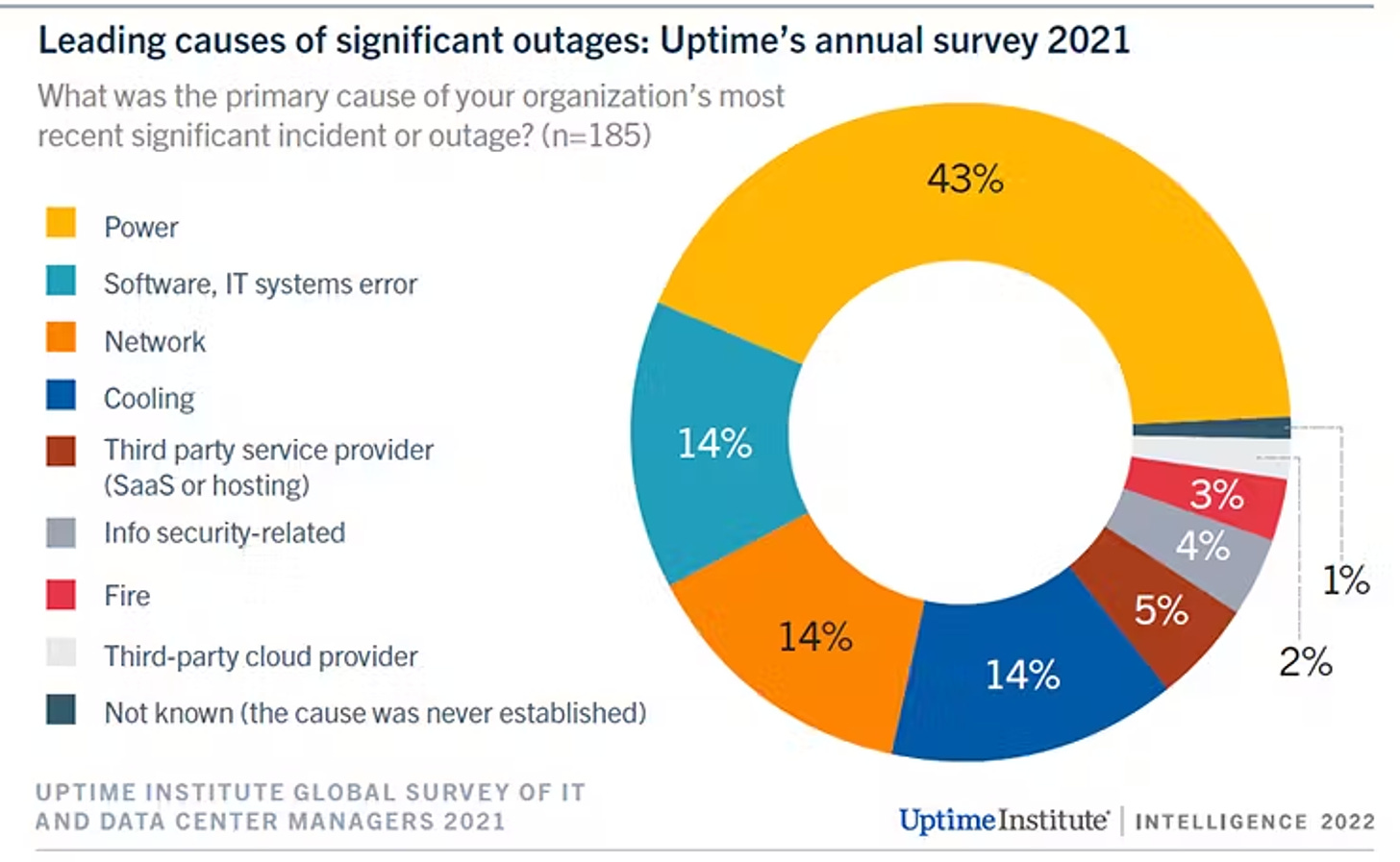
Figure 8: Leading causes of data center outages [13]



