Extended Reality (XR) Experience
In spatial computing, XR (Extended Reality) functions as a key technology that bridges the gap between the digital and physical worlds, enabling interactive experiences that are visually and contextually integrated with the user's environment. XR encompasses VR (Virtual Reality), AR (Augmented Reality), and MR (Mixed Reality), each providing unique ways to augment, simulate, or merge real and virtual scenes. This integration allows for applications such as immersive training environments, enhanced retail shopping experiences, and sophisticated remote collaboration in real-time.
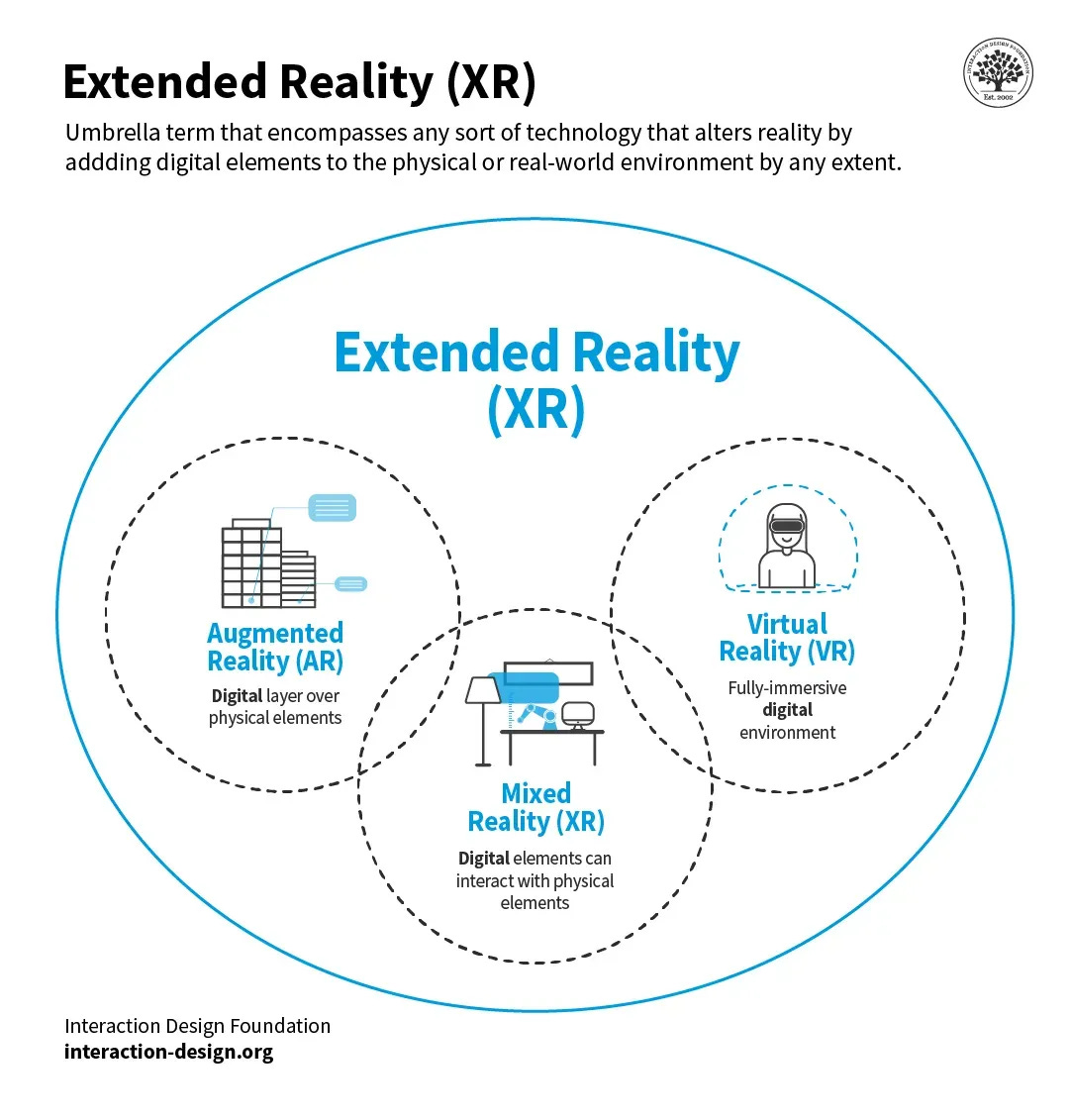
Figure 10: The term XR includes AR, MR, VR, and any technology that blends the physical and the digital world. [6]
Augmented Reality (AR)
- Description: AR overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their environment. It blends virtual elements with the physical world in real time.
- Examples: Pokémon Go, IKEA Place app, and AR navigation systems.
Sector to Watch: Mobile AR
Mobile augmented reality (AR) integrates digital content with the physical world through the camera of a mobile device. It overlays digital information such as images, text, or interactive data onto the real-world environment as seen through the device’s screen. This overlay dynamically updates as the user moves their device, providing real-time interaction with both physical and virtual elements.
Use Cases of Mobile AR:
- Retail: Consumers can use mobile AR to compare product features, prices, and reviews by scanning items with their smartphones.
- Education: AR brings educational content to life with interactive elements, enhancing engagement and learning.
- Field Services: Technicians and engineers can see schematics or repair instructions overlaid directly onto the equipment they are servicing.
- Logistics: In warehouses, AR can guide workers to specific locations and provide picking instructions, improving efficiency.
Advantages of Mobile AR:
- Enhanced User Engagement: Merging digital and physical views, AR creates compelling user experiences that are both informative and interactive.
- Accessibility: Utilizes everyday smartphones and tablets, making it widely accessible without the need for additional specialized hardware.
- Versatility: Applicable across various fields from gaming to professional training, offering practical and entertainment value.

